This compact step-up (or boost) regulator generates 3.3 V from voltages as low as 0.8 V and delivers up to 200 mA, making it perfect for powering small 3.3 V electronics projects from one or two NiMH, NiCd, or alkaline cells.
Special Order
Shipping from $9.90
+120 more from our supplier in 7-10 days
Our Code: MCU-60119
Supplier Link: [Pololu MPN:2114]
This compact step-up (or boost) regulator generates 3.3 V from voltages as low as 0.8 V and delivers up to 200 mA, making it perfect for powering small 3.3 V electronics projects from one or two NiMH, NiCd, or alkaline cells.
Discontinuation notice: The NCP1402 IC used by this voltage regulator has been discontinued by the manufacturer. We strongly recommend our newer 5V U1V10F5 and 3.3V U1V10F3 boost regulators as alternatives. The U1V10Fx voltage regulators are smaller, more efficient, have a lower minimum operating voltage, and can deliver significantly more current than the NCP1402-based regulators. These newer regulators also automatically switch into linear down-regulation mode when the input voltage exceeds the output.
These tiny boost (step-up) switching regulators are based on the NCP1402 boost regulator IC. Their small dimensions of just 0.33″ × 0.5″ (8.4 mm × 12.7 mm) and a startup voltage of down to 0.8 V make it easy to build 3.3 V and 5 V circuits that are powered by lower battery voltages. The available output current and output voltage ripple depend on the input voltage (see Typical Efficiency and Output Current section below), but the regulator can provide up to 200 mA if the input voltage is high enough.
With low input voltages, the output voltage ripple is under 40 mV peak-to-peak. When the input voltage is close to the output, the output ripple quickly climbs to 150 mV peak-to-peak. Therefore, adding capacitance from the output to ground is recommended for noise-sensitive applications with input voltages close to the output voltage.
Some example applications include:
This regulator is available with a fixed 3.3 V or 5 V output.
For higher-power applications, consider using one of our adjustable boost regulators or our U3V12Fx boost regulators. For a regulator that supports similarly low input voltages but higher currents, consider our U1V11x boost regulators, which offer features that the rest of our boost regulators lack, such as a true shutdown and automatic linear down-regulation when the input voltage exceeds the output voltage.
The boost regulator has just three connections: the input voltage, ground, and the output voltage. These three connections are labelled on the back side of the PCB and they are arranged with a 0.1″ spacing along the edge of the board for compatibility with standard solderless breadboards and perfboards and connectors that use a 0.1″ grid. You can solder wires directly to the board or solder in either the 3×1 straight male header strip or the 3×1 right-angle male header strip that are included.
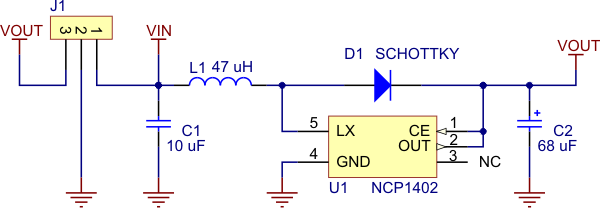 |
Pololu step-up voltage regulator NCP1402 schematic diagram. |
|---|
The efficiency of a voltage regulator, defined as (Power out)/(Power in), is an important measure of its performance, especially when battery life or heat are concerns. As shown in the graphs below, this switching regulator typically has an efficiency of 75% to 90%.
The maximum achievable output current is approximately proportional to the ratio of the input voltage to the output voltage. With a 0.8 V input, approximately 5 mA are available before the output voltage begins dropping. The full 200 mA output can be realised from input voltages over approximately 2.4 V (3.3 V version) or 2.7 V (5 V version). Additionally, the maximum output current can depend on other factors, including the ambient temperature, air flow, and heat sinking.
When connecting voltage to electronic circuits, the initial rush of current can cause damaging voltage spikes that are much higher than the input voltage. In our tests with typical power leads (~30″ test clips), input voltages above 4 V caused voltage spikes in excess of 6 V, the absolute maximum voltage of the NCP1402. You can suppress such spikes by soldering a 33 μF or larger electrolytic capacitor close to the regulator between VIN and GND.
More information about LC spikes can be found in our application note, Understanding Destructive LC Voltage Spikes.
| Size: | 0.5" x 0.33" x 0.15"1 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 0.6 g1 |
| Minimum operating voltage: | 0.8 V |
|---|---|
| Maximum operating voltage: | 3.3 V |
| Maximum output current: | 200 mA2 |
| Output voltage: | 3.3 V |
| Reverse voltage protection?: | N |
| Maximum quiescent current: | 1 mA3 |
| PCB dev codes: | reg02a |
|---|---|
| Other PCB markings: | 0J1212 |
This DXF drawing shows the locations of all of the board’s holes.
The NCP1402 will effectively remove itself from the circuit when the input voltage is higher than the output, leaving the output connected to the input through the inductor and diode. Since each of these components add a bit of voltage drop, the output voltage becomes a bit under the input voltage.
The NCP1402 has an absolute maximum voltage of 6 V, and most 5 V components can take up to 5.25 V or 5.5 V, so the 5 V regulator can be used with four NiMH or NiCd cells, which can reach 5.5 V when fully charged.