This small NEMA 8-size hybrid bipolar stepping motor has a 1.8° step angle (200 steps/revolution). Each phase draws 600 mA at 3.9 V, allowing for a holding torque of 180 g-cm (2.5 oz-in). With a weight of 60 g, this is one of the smallest stepper motors we carry.
In stock in Australia
Shipping from $9.90
+145 more from our supplier in 7-10 days
Our Code: MEC-30064
Supplier Link: [Pololu MPN:1204]
This small NEMA 8-size hybrid bipolar stepping motor has a 1.8° step angle (200 steps/revolution). Each phase draws 600 mA at 3.9 V, allowing for a holding torque of 180 g-cm (2.5 oz-in). With a weight of 60 g, this is one of the smallest stepper motors we carry.
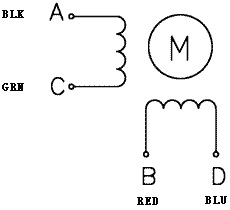 |
Bipolar stepper motor wiring diagram. |
|---|
This small hybrid bipolar stepping motor has a 1.8° step angle (200 steps/revolution). Each phase draws 600 mA at 3.9 V, allowing for a holding torque of 180 g-cm (2.5 oz-in). The motor has four colour-coded wires terminated with bare leads: black and green connect to one coil; red and blue connect to the other. These leads connect to the stepper motor through a removable JST-ZHR-5 connector. The motor can be controlled by a pair of suitable H-bridges (one for each coil), but we recommend using a bipolar stepper motor driver or one of our Tic Stepper Motor Controllers. In particular, the Tics make control easy because they support six different interfaces (USB, TTL serial, I²C, RC, analogue voltages, and quadrature encoder) and are configurable over USB with our free configuration utility.
Our 4 mm universal mounting hub can be used to mount objects on the stepper motor’s 4 mm-diameter output shaft. For a slightly more powerful motor in the same NEMA size but a longer length, consider Stepper Motor: Bipolar, 200 Steps/Rev, 20×42mm, 4.3V, 0.8 A/Phase. A comparison between these two motors can be seen in the image below.
More specifications are available in the datasheet (51k pdf).
The following diagram shows the stepper motor dimensions in mm. The dimension labelled “Length” is 30 mm. The output D-shaft has a length of 15 mm and a 4 mm diameter with a section that is flattened by 0.5 mm. This shaft works with our 4 mm universal mounting hub.
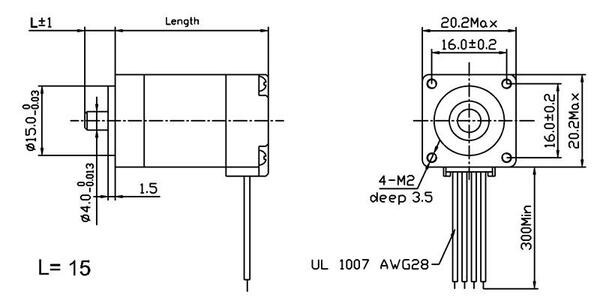 |
Stepper motors are generally used in a variety of applications where precise position control is desirable and the cost or complexity of a feedback control system is unwarranted. Here are a few applications where stepper motors are often found:
 |
Pololu’s assortment of stepper motors. |
|---|
Note: This stepper motor is SOYO part number SY20STH30-0604A.
| Size: | 20 mm square × 30 mm1 |
|---|---|
| NEMA size: | 8 |
| Weight: | 60 g |
| Shaft diameter: | 4 mm |
| Shaft type: | 4 mm "D" |
|---|---|
| Current rating: | 600 mA2 |
| Voltage rating: | 3.9 V |
| Holding torque: | 2.5 oz·in |
| Steps per revolution: | 200 |
| Resistance: | 6.5 Ohm2 |
| Inductance per phase: | 1.7 mH |
| Number of leads: | 4 |
| Lead length: | 30 cm |
Yes. To avoid damaging your stepper motor, you want to avoid exceeding the rated current, which is 600 mA in this instance. All of our stepper motor drivers let you limit the maximum current, so as long as you set the limit below the rated current, you will be within spec for your motor, even if the voltage exceeds the rated voltage. The voltage rating is just the voltage at which each coil draws the rated current, so the coils of your stepper motor will draw 600 mA at 3.9 V. By using a higher voltage along with active current limiting, the current is able to ramp up faster, which lets you achieve higher step rates than you could using the rated voltage.
If you do want to use a lower motor supply voltage for other reasons, consider using our DRV8834 or STSPIN-220 low-voltage stepper motor drivers.