The Pololu Zumo 2040 robot is a versatile tracked robot based on the Raspberry Pi RP2040 MCU. This version includes two 100:1 HP micro metal gearmotors along with integrated dual motor drivers, quadrature encoders, line sensors, side and front proximity sensors for detecting objects, a full IMU ...
Special Order
Shipping from $9.90
+60 more from our supplier in 7-10 days
Our Code: SKU-010222
Supplier Link: [Pololu MPN:5013]
The Pololu Zumo 2040 robot is a versatile tracked robot based on the Raspberry Pi RP2040 MCU. This version includes two 100:1 HP micro metal gearmotors along with integrated dual motor drivers, quadrature encoders, line sensors, side and front proximity sensors for detecting objects, a full IMU for detecting impacts and tracking orientation, six RGB LEDS, and a graphical OLED display. The low-profile robot is less than 10 cm × 10 cm—small enough to qualify for Mini Sumo. No soldering or assembly is required; just add 4 AA batteries and connect it to a computer with a USB-C cable and your Zumo is ready for programming.
The Zumo 2040 is a highly integrated, user-programmable and customisable tracked robot. It measures less than 10 cm on each side and weighs approximately 275 g with batteries (160 g without), so it is both small enough and light enough to qualify for Mini-Sumo competitions, but its versatility makes it capable of much more than just robot sumo battles.
At the heart of the Zumo 2040 is a Raspberry Pi RP2040 microcontroller (like the one on the Raspberry Pi Pico), a 32-bit dual-core Arm Cortex-M0+ processor running at 125 MHz, which can be programmed with C, C++, Arduino, or Python. The Zumo 2040 has 16 MB (128 Mbit) of flash memory that ships preloaded with a MicroPython interpreter, so you can get started right away by plugging into its USB-C port and editing the included example Python programs. For advanced users who want to customise or enhance their robots with additional peripherals, the robot’s power rails and microcontroller’s I/O lines can be accessed via 0.1″-spaced through-holes along the sides and front of the main board. A 4-pin JST SH-compatible connector that works with our 4-pin JST SH-style cables provides access to the RP2040’s I2C0 bus and can be used with many SparkFun Qwiic and Adafruit STEMMA QT devices.
The Zumo 2040 features two H-bridge motor drivers and a variety of integrated sensors, including a pair of quadrature encoders for closed-loop motor control, a complete inertial measurement unit (3-axis accelerometer, gyro, and magnetometer), five downwards-facing reflectance sensors for line-following or edge-detection, and front- and side-facing proximity sensors for obstacle detection and ranging. Three on-board pushbuttons offer a convenient interface for user input, and a 128×64 graphical OLED display, buzzer, and six RGB LEDs allow the robot to provide feedback.
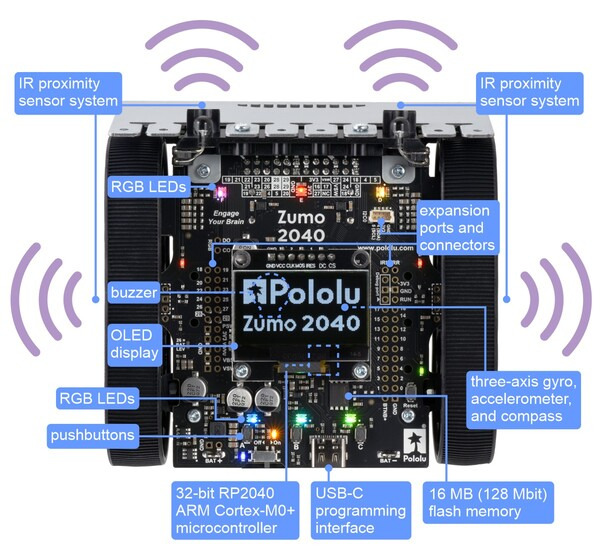  |
Zumo 2040 Robot features, top view. |
|---|
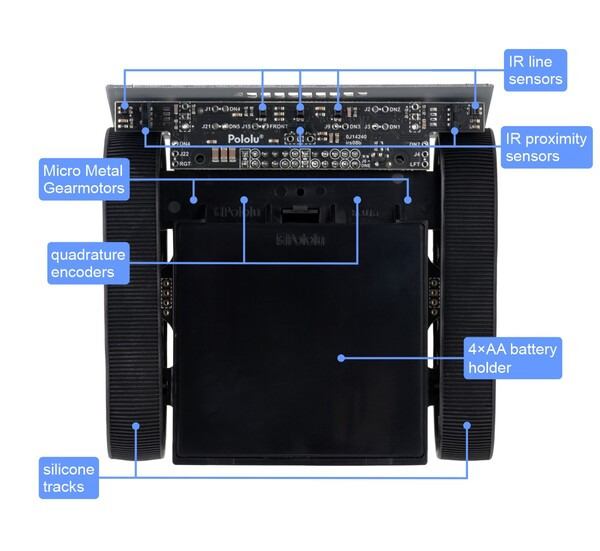  |
Zumo 2040 Robot features, bottom view. |
|---|
The Zumo 2040 robot is available fully assembled with three different motor options (see the Motors section below for more information on how these different gear ratios perform):
The Zumo 2040 robot is also available as a kit (without motors) for those who would prefer to assemble it themselves or who want to use different motors than those in the three assembled versions.
This version of the Zumo 2040 robot (item #5013) ships fully assembled with a pair of 100:1 HP micro metal gearmotors (with extended motor shafts). As described above, two assembled versions are also available with lower gear ratios (so they are both faster but cannot deliver as much torque).
You can use the following table to compare these three gear ratios in more detail. The first four columns are specifications of the motors themselves, while the last column is the measured top speed of a Zumo chassis loaded to a weight of 500 g (i.e. the maximum allowed for Mini Sumo) and driven with these motors. Note that the specifications are for 6V operation, which is approximately the voltage you would get with four alkaline batteries; four NiMH AA cells will typically provide less than 5V.
| Micro Metal Gearmotor |
Free-Run Speed @ 6V |
Stall Torque @ 6V |
Stall Current @ 6V |
Top Zumo Speed @ 6V and 500g |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50:1 HP or 50:1 HPCB | 625 RPM | 15 oz·in | 1600 mA | 40 in/s | (100 cm/s) |
| 75:1 HP or 75:1 HPCB | 400 RPM | 22 oz·in | 1600 mA | 25 in/s | (65 cm/s) |
| 100:1 HP or 100:1 HPCB | 320 RPM | 30 oz·in | 1600 mA | 20 in/s | (50 cm/s) |
  |
The Zumo robot runs off of four AA batteries. It works with both alkaline and NiMH batteries, though we recommend using rechargeable AA NiMH cells.
|
|
|
| Size: | 96L × 99W × 39H mm |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 160 g1 |
| Processor: | RP2040 @ 125 MHz |
|---|---|
| RAM size: | 264 Kbytes |
| Program memory size: | 16 Mbytes |
| External programmer required?: | N |
| Assembled: | Y |
| Version: | assembled with 100:1 HP motors |
| PCB dev codes: | zum03a |
|---|---|
| Other PCB markings: | 0J14237 |
User’s manual for the Pololu Zumo 2040 robot.
This model uses simplified models of the control electronics to reduce the file size. More detailed models are available separately of the Zumo 2040 Main Board (23MB step) and Zumo 2040 Front Sensor Array (6MB step).
This DXF drawing shows the locations of all of the board’s holes.
This repository contains libraries and example code for the Pololu Zumo 2040 Robot in MicroPython and C.